 18 May
18 MayAll in 1 Guide to Flea and Tick Prevention for Pets: Protecting Your Furry Friends Year-Round
Table of Contents
Flea and tick prevention for pets has become one of the most critical aspects of responsible pet ownership. These tiny parasites pose significant health risks to dogs and cats, making comprehensive prevention strategies essential for every pet parent. Understanding effective flea and tick prevention for pets not only protects your beloved companions but also safeguards your family and home environment from these persistent pests.
Understanding the Importance of Flea and Tick Prevention for Pets
When we discuss flea and tick prevention for pets, we’re addressing a multifaceted health concern that extends beyond simple pest control. Fleas and ticks are more than annoying insects they’re vectors for serious diseases that can compromise your pet’s well-being and, in some cases, threaten human health as well.
The significance of implementing robust flea and tick prevention for pets becomes apparent when considering the rapid reproduction rate of these parasites. A single female flea can lay up to 50 eggs daily, meaning a small infestation can quickly spiral into a major problem without proper preventive measures. Similarly, ticks can transmit dangerous pathogens within hours of attachment, making prevention far more effective than treatment after exposure.
Modern veterinary medicine has developed sophisticated approaches to flea and tick prevention for pets, offering pet owners numerous options to protect their companions. From topical treatments to oral medications, the arsenal against these parasites has never been more comprehensive or effective.
The Complex Lifecycle and Behavior of Fleas and Ticks
Understanding the lifecycle of fleas and ticks is fundamental to effective flea and tick prevention for pets. These parasites have evolved sophisticated survival strategies that make them remarkably persistent and challenging to eliminate once established.
Flea Lifecycle and Environmental Impact
The flea lifecycle consists of four distinct stages: egg, larva, pupa, and adult. This complete metamorphosis typically takes 14-35 days under optimal conditions, though environmental factors can extend this period significantly. Adult fleas represent only about 5% of the total flea population in any given environment, with the remaining 95% consisting of eggs, larvae, and pupae hidden throughout your home.
When addressing flea and tick prevention for pets, it’s crucial to understand that fleas spend the majority of their lifecycle off your pet. After feeding and mating on your dog or cat, female fleas lay eggs that fall off into carpeting, bedding, furniture cracks, and yard debris. These eggs hatch into larvae that feed on organic matter, including adult flea feces, skin cells, and other debris.
The pupal stage presents particular challenges for flea and tick prevention for pets because pupae are protected by cocoons that are resistant to many treatments. Adult fleas can remain in these cocoons for weeks or even months, emerging when they detect vibrations, carbon dioxide, or heat signals indicating a potential host is nearby.
Tick Behavior and Disease Transmission
Ticks exhibit different behaviors depending on their species and life stage. Hard ticks, which include species that transmit Lyme disease, Rocky Mountain spotted fever, and ehrlichiosis, use a hunting strategy called “questing.” They climb onto vegetation and extend their front legs, waiting to latch onto passing hosts.
Effective flea and tick prevention for pets must account for tick behavior patterns throughout their lifecycle. Ticks require blood meals to progress from larva to nymph to adult, and each feeding can last several days. This extended feeding period increases the risk of disease transmission, making prevention strategies more critical than post-exposure treatments.
Unlike fleas, ticks don’t reproduce on their hosts. After feeding, they drop off to molt or lay eggs in the environment. However, their ability to survive for extended periods without feeding sometimes over a year makes environmental management a crucial component of comprehensive flea and tick prevention for pets.
Health Risks and Disease Transmission
The health implications of inadequate flea and tick prevention for pets extend far beyond simple irritation and discomfort. These parasites serve as vectors for numerous serious diseases that can affect both pets and humans, making prevention a public health concern as well as an animal welfare issue.
Flea-Borne Diseases and Complications
Fleas transmit several diseases that can severely impact your pet’s health. Flea Allergy Dermatitis (FAD) represents one of the most common complications of flea infestation. This allergic reaction to flea saliva can cause intense itching, skin inflammation, and secondary bacterial infections. Pets with FAD may develop hot spots, excessive scratching behaviors, and hair loss that persists long after flea elimination.
Bartonellosis, commonly known as cat scratch disease, can be transmitted by fleas between cats and potentially to humans. While often asymptomatic in cats, this bacterial infection can cause fever, lethargy, and lymph node swelling in humans, particularly children and immunocompromised individuals.
In severe infestations, especially in young, elderly, or debilitated pets, fleas can cause anemia through blood loss. This condition, known as flea anemia, can be life-threatening and demonstrates why consistent flea and tick prevention for pets is essential rather than optional.
Tick-Borne Diseases and Their Consequences
Ticks transmit a broader range of serious diseases than fleas, making tick prevention particularly critical. Lyme disease, transmitted by black-legged ticks, can cause lameness, fever, loss of appetite, and kidney problems in dogs. While less common in cats, feline Lyme disease can still occur and cause similar symptoms.
Ehrlichiosis and anaplasmosis affect white blood cells and platelets, respectively, leading to symptoms including fever, lethargy, loss of appetite, and bleeding disorders. Rocky Mountain spotted fever, despite its name, occurs throughout the United States and can cause fever, arthritis, and in severe cases, neurological complications.
Babesiosis, caused by microscopic parasites that infect red blood cells, can lead to anemia, jaundice, and organ failure. This disease particularly affects dogs and can be fatal without prompt treatment, highlighting the importance of proactive flea and tick prevention for pets.
Cross-Species Disease Transmission
Many tick-borne diseases are zoonotic, meaning they can transmit from animals to humans. This characteristic makes flea and tick prevention for pets a family health issue. Lyme disease, Rocky Mountain spotted fever, ehrlichiosis, and anaplasmosis can all affect humans, often with more severe consequences than in pets.
While direct transmission from pets to humans is uncommon, pets can bring infected ticks into the home environment, increasing human exposure risk. Additionally, pets with tick-borne diseases may require extensive treatment that can be emotionally and financially taxing for pet owners.
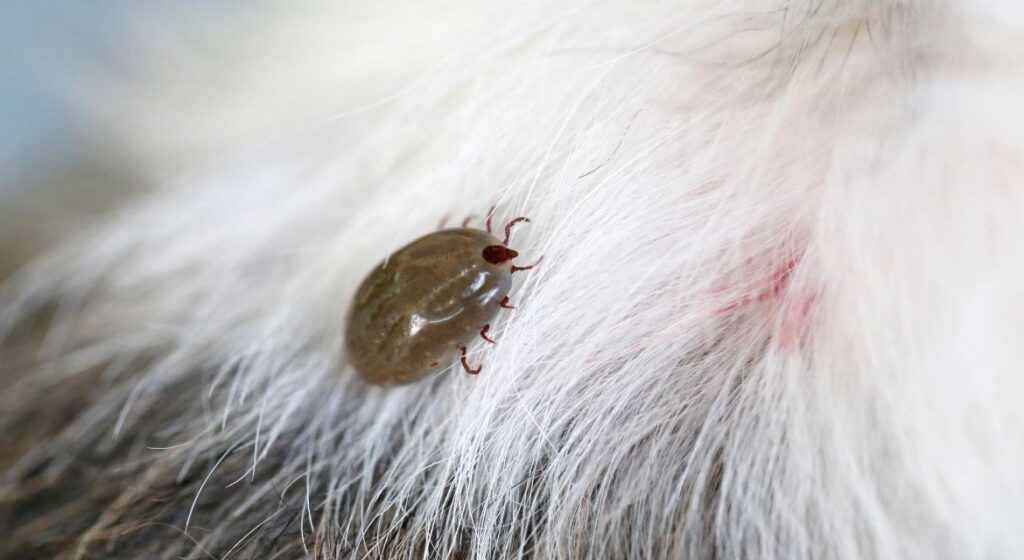
Recognizing Early Signs of Flea and Tick Infestation
Early detection is crucial for effective flea and tick prevention for pets because it allows for prompt intervention before infestations become established. Pet owners should regularly monitor their animals for signs of parasite activity and understand how to distinguish between normal scratching and indicators of potential problems.
Visual and Behavioral Indicators
Increased scratching, licking, or biting at specific body areas often represents the first sign of flea activity. Pets may focus their attention on the base of the tail, inner thighs, abdomen, and neck areas where fleas commonly congregate. However, pets with flea allergies may scratch at any location due to systemic allergic reactions.
Flea dirt, which appears as small black specks in your pet’s fur, provides definitive evidence of flea infestation. This material consists of digested blood excreted by adult fleas and turns reddish-brown when moistened with water. Finding flea dirt indicates active flea feeding and the need for immediate implementation of flea and tick prevention for pets protocols.
Hair loss patterns can indicate both flea and tick problems. Fleas typically cause patchy hair loss from excessive scratching, while tick attachment sites may show localized hair loss with associated skin irritation. Red, inflamed skin or the development of hot spots should prompt immediate veterinary consultation and evaluation of your current flea and tick prevention for pets strategy.
Physical Examination Techniques
Regular physical examinations form an essential component of comprehensive flea and tick prevention for pets. Run your hands through your pet’s fur, feeling for unusual bumps or irregularities that might indicate tick attachment. Pay particular attention to areas with less fur, such as the ears, neck, armpits, and between toes, where ticks commonly attach.
Use a fine-toothed flea comb to check for adult fleas and flea dirt. Focus on areas where your pet cannot easily groom, such as the head, neck, and base of the tail. Combing should be performed over a white towel or paper to make any fleas or debris more visible.
Check for signs of skin irritation, unusual odors, or changes in your pet’s coat condition. These indicators may suggest developing problems that require adjustment of your flea and tick prevention for pets approach. Remember that some pets may not show obvious signs of infestation, making regular preventive treatments essential regardless of apparent symptoms.
Comprehensive Prevention Strategies
Effective flea and tick prevention for pets requires a multi-modal approach that addresses various aspects of parasite control. No single method provides complete protection, making integrated prevention strategies the most reliable approach to keeping your pets healthy and comfortable.
Professional Veterinary Care and Consultation
Regular veterinary consultations form the foundation of any effective flea and tick prevention for pets program. Your veterinarian can assess your pet’s individual risk factors, including age, health status, lifestyle, and geographic location, to develop a customized prevention plan.
During routine examinations, veterinarians can detect early signs of parasite-related health issues that owners might miss. They can also evaluate the effectiveness of current prevention methods and make adjustments based on seasonal changes, travel plans, or evolving parasite populations in your area.
Professional veterinary care includes access to prescription-strength treatments that often provide superior efficacy compared to over-the-counter options. Many prescription products offer longer-lasting protection and broader spectrum coverage against multiple parasite species, making them valuable components of comprehensive flea and tick prevention for pets strategies.
Veterinarians stay current with emerging research on parasite resistance, new product developments, and changing disease patterns in local areas. This expertise ensures that your flea and tick prevention for pets approach remains effective against current threats and incorporates the latest advances in parasitology and preventive medicine.
Topical and Spot-On Treatments
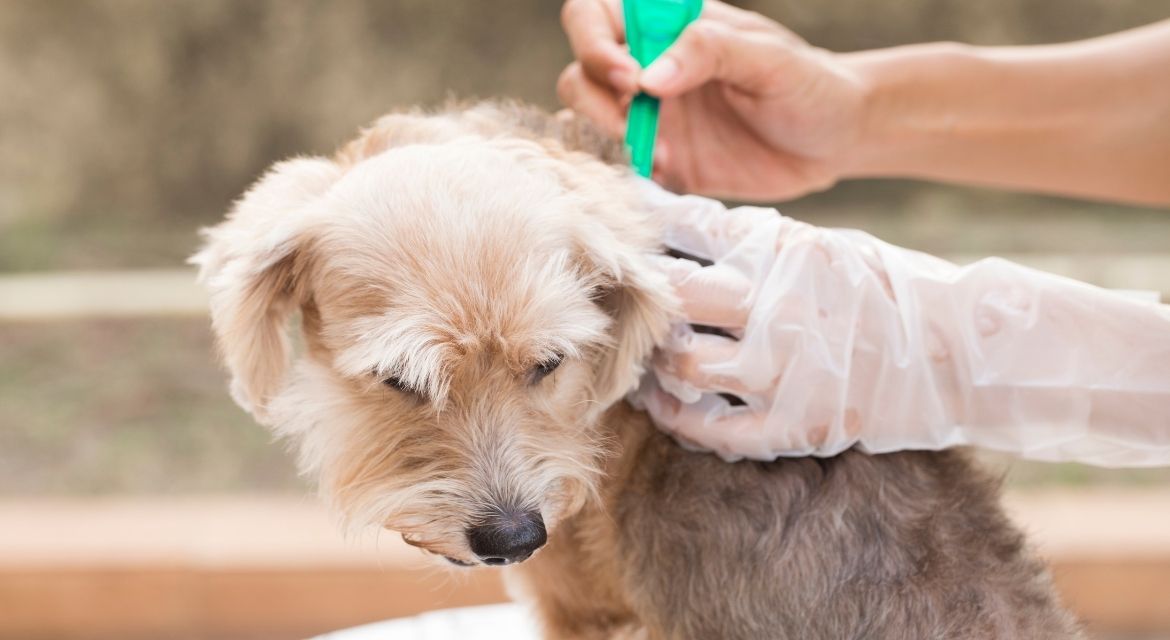
Topical treatments represent one of the most popular and effective methods for flea and tick prevention for pets. These products, applied between the shoulder blades or along the spine, distribute through the pet’s skin and provide systemic protection against parasites.
Modern spot-on treatments offer several advantages for flea and tick prevention for pets, including ease of application, long-lasting protection, and broad-spectrum efficacy. Most products provide protection for 30 days, though some newer formulations extend coverage to 3 months or longer.
The active ingredients in topical treatments work through different mechanisms. Some products kill parasites on contact, while others require parasites to bite the pet before taking effect. Understanding these differences helps optimize flea and tick prevention for pets based on your specific circumstances and parasite pressures.
Application technique significantly impacts the effectiveness of topical flea and tick prevention for pets products. The medication must reach the skin, not just the fur, and should be applied to areas your pet cannot lick. Following manufacturer instructions precisely ensures optimal protection and minimizes the risk of adverse reactions.
Oral Medications and Systemic Treatments
Oral medications have revolutionized flea and tick prevention for pets by offering convenient, highly effective protection that doesn’t depend on topical application. These products work systemically, circulating through your pet’s bloodstream to kill parasites when they feed.
Chewable tablets provide excellent compliance for flea and tick prevention for pets because many products are flavored to be palatable and can be given as treats. This delivery method eliminates concerns about washing off topical treatments or protecting application sites from children or other pets.
Different oral medications target parasites through various mechanisms. Some interfere with the nervous systems of fleas and ticks, while others disrupt their reproductive cycles or affect their ability to feed effectively. Understanding these differences helps veterinarians select the most appropriate oral options for your specific flea and tick prevention for pets needs.
The rapid onset of action characterizes many oral flea and tick prevention for pets products. Some medications begin killing fleas within hours of administration, providing quick relief for pets with existing infestations while preventing new parasite establishment.
Collar-Based Prevention Systems
Flea and tick prevention collars offer continuous protection through slow release of active ingredients over several months. Modern collar systems provide effective flea and tick prevention for pets while addressing many concerns associated with older collar technologies.
Contemporary prevention collars distribute active ingredients through contact with your pet’s skin and fur, creating a protective zone around the entire body. This distribution method provides comprehensive coverage that can be particularly effective for flea and tick prevention for pets in high-risk environments.
The convenience of collar-based flea and tick prevention for pets makes them attractive for busy pet owners or those with multiple animals. Once applied, collars provide continuous protection without requiring monthly applications or daily medications, reducing the likelihood of missed doses.
Safety considerations for collar-based flea and tick prevention for pets include proper sizing, regular monitoring for skin irritation, and ensuring the collar can break away if caught on objects. Modern collars incorporate safety features and use active ingredients with improved safety profiles compared to older formulations.
Environmental Management and Control
Environmental control measures play a crucial role in comprehensive flea and tick prevention for pets because these parasites spend significant portions of their lifecycles off your pet. Addressing environmental reservoirs of parasites prevents reinfestation and reduces the overall parasite burden in your pet’s living space.
Indoor Environmental Treatment
Indoor environments can harbor large populations of developing fleas, making thorough indoor treatment essential for effective flea and tick prevention for pets. Regular vacuuming removes eggs, larvae, and pupae from carpeting, upholstery, and cracks where they accumulate. The vibration and suction of vacuuming also stimulate flea emergence from cocoons, making them susceptible to treatments.
Washing pet bedding, toys, and removable fabric items in hot water (140°F or higher) kills all flea life stages. The heat treatment should be followed by hot drying cycles to ensure complete elimination. This approach provides an important complement to chemical treatments in comprehensive flea and tick prevention for pets programs.
Indoor environmental sprays and treatments can eliminate flea populations in areas where pets spend time. Products containing insect growth regulators prevent flea development and provide long-lasting residual effects. However, these treatments should be integrated with other flea and tick prevention for pets methods rather than used as standalone solutions.
Humidity control impacts flea development because low humidity levels inhibit egg hatching and larval survival. Maintaining indoor humidity below 50% during dry months can significantly reduce flea populations and support overall flea and tick prevention for pets efforts.
Outdoor Yard and Garden Management
Outdoor environments present particular challenges for flea and tick prevention for pets because weather, wildlife, and vegetation create favorable conditions for parasite development. Regular yard maintenance, including keeping grass short and removing leaf litter, reduces habitat for developing ticks and fleas.
Landscaping choices can support flea and tick prevention for pets by reducing parasite-friendly environments. Creating barriers between wooded areas and recreational spaces, using gravel or wood chips around patios, and removing dense vegetation near the home reduces parasite encounters during outdoor activities.
Yard treatments for flea and tick prevention for pets should focus on areas where pets spend the most time, such as around patios, dog runs, and favorite resting spots under trees or decks. Professional pest control services can provide targeted treatments that complement individual pet protection measures.
Wildlife management plays an important role in outdoor flea and tick prevention for pets because wild animals serve as hosts for these parasites. Removing attractants like bird feeders near the house, securing garbage containers, and installing fencing can reduce wildlife traffic through your yard.
Seasonal Considerations and Timing
Seasonal variations in parasite activity require adjustments to flea and tick prevention for pets strategies throughout the year. While year-round prevention is recommended in most climates, understanding seasonal patterns helps optimize treatment timing and intensity.
Spring emergence of overwintering parasites often creates the highest risk periods for flea and tick prevention for pets. Implementing intensive prevention measures before peak activity seasons provides better protection than reactive treatments after problems develop.
Fall prevention measures for flea and tick prevention for pets should account for parasites seeking overwintering sites. Treating both pets and environments during this transition period prevents establishment of parasite populations that will emerge the following spring.
Geographic location significantly influences seasonal flea and tick prevention for pets strategies. Consult with local veterinarians about regional parasite patterns, peak activity periods, and locally effective prevention approaches to optimize your pet’s protection.
Natural and Alternative Prevention Approaches
While conventional treatments form the core of effective flea and tick prevention for pets, natural and alternative approaches can provide supplementary benefits or serve as adjuncts to traditional therapies. Understanding the capabilities and limitations of these methods helps pet owners make informed decisions about incorporating them into their prevention strategies.
Essential Oils and Plant-Based Repellents
Certain essential oils demonstrate repellent properties against fleas and ticks, offering natural options for flea and tick prevention for pets. Cedar oil, peppermint oil, and rosemary oil have shown varying degrees of efficacy in laboratory and field studies. However, effectiveness is generally lower and shorter-lasting than conventional treatments.
Safety considerations are paramount when using essential oils for flea and tick prevention for pets. Cats are particularly sensitive to many essential oils due to their unique metabolism, which cannot effectively process certain compounds. Always consult with veterinarians before using essential oil-based products, especially on cats or pets with health conditions.
Dilution and application methods significantly impact both safety and efficacy of essential oil-based flea and tick prevention for pets. Commercial products formulated specifically for pets undergo safety testing and provide appropriate concentrations, while homemade preparations may pose risks if improperly prepared.
While essential oils may provide some repellent effect for flea and tick prevention for pets, they should not replace proven conventional treatments in high-risk situations or for pets with existing parasite-related health issues.
Dietary Supplements and Nutritional Approaches
Various dietary supplements are marketed for flea and tick prevention for pets, including B vitamins, garlic, brewer’s yeast, and omega fatty acids. While these products are generally safe, scientific evidence supporting their effectiveness as primary prevention methods remains limited.
Some nutritional approaches may support overall skin health and immune function, potentially making pets less attractive to parasites or more resistant to parasite-related health issues. However, these benefits typically complement rather than replace conventional flea and tick prevention for pets measures.
Garlic supplements require particular caution for flea and tick prevention for pets because large quantities can cause toxicity, particularly in cats and small dogs. If considering garlic-based products, consult with veterinarians about appropriate dosing and safety considerations.
Omega fatty acid supplementation may support skin barrier function and reduce inflammatory responses to parasite bites, providing indirect benefits for flea and tick prevention for pets. These supplements also offer additional health benefits for coat quality and joint health.
Physical and Mechanical Prevention Methods
Regular grooming and inspection provide important mechanical support for flea and tick prevention for pets. Fine-toothed flea combs can remove adult fleas and ticks, while regular brushing helps detect parasites early and removes flea dirt and debris.
Protective clothing and accessories, such as tick-repelling bandanas or protective boots, can provide additional barriers against parasite attachment during high-risk activities. While not substitutes for systemic treatments, these items offer supplementary protection for flea and tick prevention for pets during hiking or travel to heavily infested areas.
Limiting outdoor access during peak parasite activity times can reduce exposure risk as part of comprehensive flea and tick prevention for pets strategies. Early morning and evening hours often coincide with increased tick questing behavior, while midday heat may reduce their activity levels.
Environmental modifications that reduce parasite habitat near your home support overall flea and tick prevention for pets efforts. Installing physical barriers, modifying landscaping, and controlling moisture levels create less hospitable environments for parasite development.
Product Selection and Veterinary Guidance
Choosing appropriate products for flea and tick prevention for pets requires careful consideration of multiple factors, including your pet’s health status, lifestyle, local parasite pressures, and your personal preferences. Professional veterinary guidance ensures optimal product selection and application for maximum effectiveness and safety.
Factors Influencing Product Choice
Age considerations play a crucial role in flea and tick prevention for pets because young animals may require different products or dosing than adults. Puppies and kittens often need age-appropriate formulations with modified active ingredients or application methods. Senior pets may have health conditions that influence product selection and require more careful monitoring during treatment.
Health status significantly impacts flea and tick prevention for pets product selection. Pets with liver disease, kidney dysfunction, or skin conditions may require special considerations when choosing treatments. Some products are contraindicated in pets with certain health conditions, making veterinary consultation essential for safe prevention.
Lifestyle factors influence the intensity and type of flea and tick prevention for pets needed. Outdoor pets, hunting dogs, or animals that frequently visit dog parks face higher parasite exposure and may require more robust protection than indoor pets. Travel patterns and seasonal activities also impact prevention needs.
Multi-pet households require coordinated flea and tick prevention for pets strategies that account for potential cross-contamination and different species requirements. Products safe for dogs may be toxic to cats, necessitating careful product selection and application in mixed-species households.
Comparing Commercial Products and Brands
Leading brands in flea and tick prevention for pets have developed products with different active ingredients, application methods, and duration of action. Understanding these differences helps optimize protection for your specific circumstances. Some products excel at rapid flea kill, while others provide longer-lasting protection or broader spectrum coverage.
Cost-effectiveness in flea and tick prevention for pets involves considering both initial product cost and long-term value. More expensive products may provide longer protection periods or broader coverage, potentially offering better value than cheaper alternatives requiring more frequent application.
Resistance patterns in local parasite populations may influence product effectiveness for flea and tick prevention for pets. Veterinarians can provide information about locally effective products and recommend rotations between different active ingredients to maintain efficacy.
Combination products that provide protection against multiple parasites may offer convenience and cost savings for comprehensive flea and tick prevention for pets. These products often include heartworm prevention, intestinal parasite control, or other health benefits alongside flea and tick protection.
Professional Recommendations and Customization
Veterinary professionals consider multiple factors when recommending flea and tick prevention for pets, including local disease prevalence, seasonal patterns, and individual pet risk factors. Their recommendations are based on current research, clinical experience, and knowledge of local parasite populations and resistance patterns.
Regular reassessment of flea and tick prevention for pets effectiveness allows for adjustments based on changing circumstances, new product availability, or emerging parasite resistance. Annual or biannual preventive care visits provide opportunities to evaluate and optimize prevention strategies.
Special circumstances, such as pregnancy, nursing, or recovery from illness, may require modifications to standard flea and tick prevention for pets protocols. Veterinarians can recommend safe alternatives or adjust dosing to accommodate these situations while maintaining effective protection.
Emergency consultation becomes necessary if pets develop adverse reactions to flea and tick prevention for pets products or if breakthrough infestations occur despite prevention efforts. Professional guidance ensures appropriate treatment adjustments and rapid resolution of problems.
Implementation of Year-Round Prevention Programs
Successful flea and tick prevention for pets requires consistent, year-round implementation rather than seasonal or reactive treatments. Developing systematic approaches to prevention ensures continuous protection and reduces the likelihood of parasite-related health issues affecting your pets.
Establishing Consistent Treatment Schedules
Monthly administration schedules for flea and tick prevention for pets provide reliable protection when followed consistently. Setting reminders through calendars, mobile apps, or automatic prescription delivery services helps maintain compliance and prevents gaps in protection that could allow parasite establishment.
Record-keeping systems track treatment dates, product types, and any observed changes in your pet’s health or parasite status. These records provide valuable information for veterinary consultations and help identify patterns that might indicate needed adjustments to flea and tick prevention for pets strategies.
Seasonal intensification of flea and tick prevention for pets may be appropriate in areas with distinct high-risk periods. Adding environmental treatments, increasing inspection frequency, or using combination products during peak seasons provides enhanced protection when risk is greatest.
Travel preparations require evaluation and possible modification of standard flea and tick prevention for pets protocols. Different geographic regions may have varying parasite species, disease risks, or product availability, necessitating consultation with veterinarians familiar with destination-specific risks.
Monitoring Treatment Effectiveness
Regular assessment of flea and tick prevention for pets effectiveness involves ongoing monitoring of your pet’s health, behavior, and parasite status. Changes in scratching patterns, skin condition, or energy levels may indicate needed adjustments to prevention strategies.
Environmental monitoring complements individual pet assessments in evaluating flea and tick prevention for pets effectiveness. Checking for flea dirt in pet bedding, observing parasite activity in yard areas, or noting tick presence during outdoor activities provides information about environmental parasite pressures.
Veterinary examinations provide professional evaluation of flea and tick prevention for pets effectiveness through physical examination, parasite testing, and health status assessment. These evaluations can detect subtle changes that owners might miss and guide treatment adjustments.
Documentation of prevention outcomes helps build a comprehensive picture of what works best for your individual pets and circumstances. This information proves valuable when adjusting flea and tick prevention for pets strategies or when consulting with veterinarians about optimization opportunities.
Family and Caregiver Education
Comprehensive flea and tick prevention for pets requires involvement and understanding from all family members and pet caregivers. Education about parasite risks, prevention methods, and monitoring techniques ensures consistent implementation regardless of who is caring for your pets.
Training family members to recognize signs of parasite infestation enables early detection and prompt response to potential problems. Regular family discussions about flea and tick prevention for pets help maintain awareness and compliance with prevention protocols.
Pet sitters, dog walkers, and boarding facilities should be informed about your pet’s flea and tick prevention for pets program to ensure continuity of care during your absence. Providing clear instructions and emergency contact information helps maintain protection when pets are in others’ care.
Children in the household require age-appropriate education about flea and tick prevention for pets, including the importance of not handling or removing prevention products and recognizing when pets need attention for parasite-related issues.
Advanced Considerations and Future Developments
The field of flea and tick prevention for pets continues to evolve with advances in technology, understanding of parasite biology, and development of new active ingredients. Staying informed about these developments helps optimize long-term prevention strategies and may provide new options for challenging situations.
Emerging Technologies and Treatments
Novel delivery systems for flea and tick prevention for pets include extended-release implants, wearable technology, and targeted biologics that offer potentially improved convenience and effectiveness. These technologies may provide options for pets that cannot tolerate traditional treatments or require enhanced protection.
Resistance management strategies become increasingly important as parasite populations develop resistance to commonly used active ingredients. Understanding resistance patterns and implementing appropriate rotation or combination strategies helps maintain effective flea and tick prevention for pets over time.
Precision medicine approaches to flea and tick prevention for pets may enable customization based on individual pet genetics, microbiome characteristics, or specific risk factors. These developments could optimize treatment selection and minimize adverse reactions while maximizing protection.
Environmental management technologies, including smart monitoring systems and automated treatment devices, may provide enhanced support for comprehensive flea and tick prevention for pets programs. These tools could enable real-time assessment of parasite pressures and automated responses to changing conditions.
Research and Development Trends
Current research in flea and tick prevention for pets focuses on developing new active ingredients with novel mechanisms of action, improved safety profiles, and enhanced environmental compatibility. Understanding these developments helps anticipate future treatment options and prepare for evolving parasite challenges.
Climate change impacts on parasite distribution and activity patterns require adaptive approaches to flea and tick prevention for pets. Changing temperatures, precipitation patterns, and wildlife distribution may alter traditional seasonal patterns and geographic ranges of disease-carrying parasites.
One Health approaches to flea and tick prevention for pets recognize the interconnections between animal health, human health, and environmental health. These perspectives may lead to more comprehensive prevention strategies that address multiple species and ecosystem considerations simultaneously.
Sustainable and environmentally conscious flea and tick prevention for pets options are increasingly important to many pet owners. Research into biodegradable treatments, reduced environmental impact formulations, and sustainable production methods may provide eco-friendly alternatives without compromising effectiveness.
Conclusion: Commitment to Comprehensive Protection
Effective flea and tick prevention for pets represents a fundamental responsibility of pet ownership that requires ongoing commitment, professional guidance, and adaptive management. The complexity of parasite biology, disease transmission, and prevention strategies necessitates a comprehensive approach that integrates multiple protection methods with regular assessment and adjustment.
The investment in robust flea and tick prevention for pets pays dividends in improved pet health, reduced veterinary costs, and enhanced quality of life for both pets and their families. Preventing parasite-related diseases is invariably more effective, less expensive, and less stressful than treating established infections or infestations.
Success in flea and tick prevention for pets depends on consistency, vigilance, and willingness to adapt strategies based on changing circumstances, new product availability, and evolving parasite challenges. Regular veterinary partnerships, family education, and commitment to year-round prevention form the foundation of effective protection.
As our understanding of parasite biology, disease transmission, and prevention methods continues to advance, opportunities for even more effective flea and tick prevention for pets will emerge. Staying informed about these developments and maintaining flexibility in prevention approaches ensures optimal protection for our cherished animal companions throughout their lives.
The goal of comprehensive flea and tick prevention for pets extends beyond simple parasite control to encompass whole-animal wellness, family health protection, and environmental responsibility. By embracing this broader perspective and committing to proven prevention strategies, pet owners can provide their companions with the protection they deserve while contributing to overall public health and environmental stewardship.
You May Also Like :
How to Stop Dog Barking: The Complete Guide to a Quieter, Happier Pet
Comprehensive Guide to Interactive Cat Toys: Keeping Indoor Cats Happy and Healthy
Dog Grooming at Home: The Complete Guide for Dog Owners
10 Essential Dog Training Tips Every New Puppy Owner Should Know
How to Take Care of a Pet: Essential Guide to Responsible Pet Ownership
The Ultimate Guide to Cat Playtime: Why Play Is Essential for Your Feline’s Health and Happiness
How to Successfully Work from Home with Pets: A Comprehensive Guide
The Mental Health Benefits of Having a Dog: What Every Pet Owner Should Know
How to Groom a Puppy for the First Time: Step-by-Step Guide
Quick Solutions for Daily Pet Care: Simple Strategies for a Happier Pet and Easier Routine




